Table of Contents
Let’s start this blog with an imagination!
Two crypto projects are launching on the same day. Both have smart teams, modern technology, and a lot of hype. A few months later, one of them is thriving with an active community and growth, while the other one has faded.
Do you know what decides its growth and failure? Well, it’s tokenomics!
Tokenomics is the behind-the-scenes engine that decides how a crypto token behaves. It includes everything from the creation, distribution, and supply of tokens to their utility and incentives for either holding or using these tokens.
For newbies, tokenomics may sound complicated or technical. But at its core, it’s just about understanding incentives and supply. Once you understand these basics, you will start seeing crypto projects in a completely new way.
So, want to know what tokenomics is in cryptocurrency, why it is important, and why understanding tokenomics can help you make smarter decisions? Here’s a simple tokenomics beginner guide.
There you go!
Understanding Tokenomics
Tokenomics is a combination of token and economics, which refers to the study of how a crypto token operates within the blockchain ecosystem. It includes everything from token supply and distribution to its specific use case and governance.
It determines how value is created, maintained, or destroyed in a blockchain network. Properly designed tokenomics ensure that users, developers, and investors are aligned to sustain long-term growth.
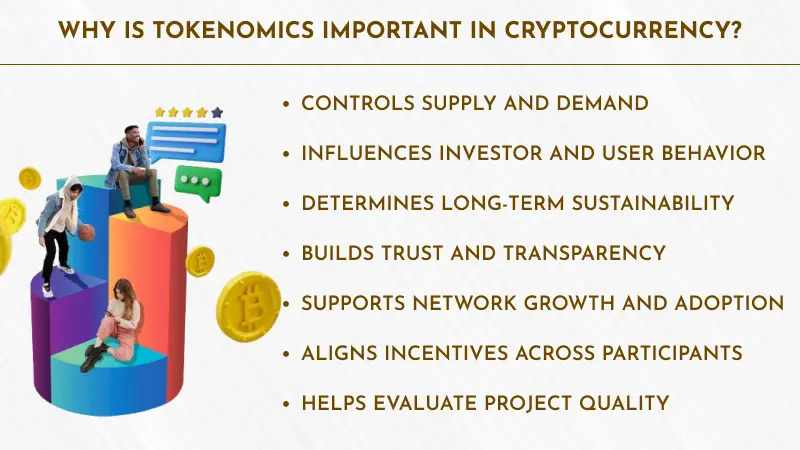
Why is Tokenomics Important in Cryptocurrency?
Tokenomics play an important role in determining whether a crypto project succeeds or fails. Let’s describe its importance!
Controls Supply and Demand
Tokenomics defines how many tokens exist, how quickly new tokens are released, and how many are available for trading at any time. These factors directly affect demand and price stability. If too many tokens enter the market too fast, prices can drop sharply, even if the project is strong.
Influences Investor and User Behavior
A well-designed token system encourages users to hold, stake, or actively use the token within the ecosystem. On the other hand, poor tokenomics often leads to quick selling and short-term speculation, which can harm the project’s long-term growth.
Determines Long-Term Sustainability
Tokenomics plays a key role in keeping a project running over time. Sustainable reward structures, controlled inflation, and ongoing demand help ensure that the network remains active and financially stable as adoption grows.
Builds Trust and Transparency
Clear information about token supply, distribution, and vesting schedules helps build trust among investors and users. When people understand how tokens are allocated and released, they are more confident in the project’s fairness and credibility.
Supports Network Growth and Adoption
Tokens with real utility encourage participation in the ecosystem, such as paying fees, accessing services, or voting on governance decisions. This active usage drives adoption and helps the network grow organically rather than relying on speculation alone.
Aligns Incentives Across Participants
Good tokenomics ensures that developers, users, validators, and investors all benefit when the network succeeds. This alignment motivates everyone involved to contribute positively to the ecosystem instead of acting only in self-interest.
Helps Evaluate Project Quality
Tokenomics provides insight into how well a project has been planned. A clear and balanced token model often reflects strong fundamentals, while unclear or unfair token structures can signal potential risks or long-term problems.
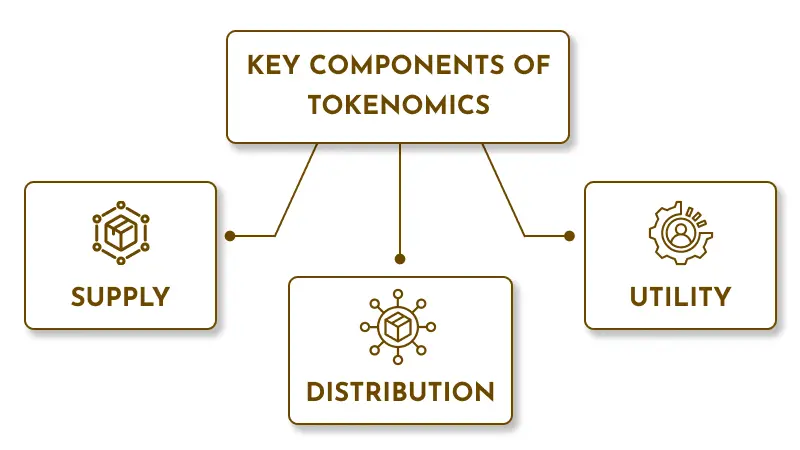
Key Components of Tokenomics
Tokenomics has several parts, and each of them plays an integral role. Let’s take a look at them!
Supply
Supply is the basis of tokenomics. It clearly shows the number of tokens that exist now or may exist in the future.
- The max supply in tokenomics shows the highest number of tokens that can ever exist.
- Total supply is the number of tokens that currently exist on the blockchain.
- The circulating supply in tokenomics means the number of tokens available in the market at any given timeframe.
Whenever the max supply is fixed for a token, users can expect a limited number of tokens. This can help support the long-term stability of tokens. And when supply grows without any limits, inflation can rise steadily.
Distribution
Distribution in tokenomics explains how tokens are allocated and released among different participants in a crypto project. It plays an important role in determining fairness, trust, and long-term sustainability.
Token distribution usually includes allocations for:
- Founders and core team
- Early investors and advisors
- Public sale participants
- Community rewards and ecosystem growth
A well-planned distribution ensures that no single group controls too many tokens at once. This helps prevent price manipulation and sudden sell-offs.
Utility
Utility defines what a token is actually used for within the ecosystem. Without real utility, a token often becomes purely speculative and struggles to maintain long-term value.
Token utility can include:
- Paying transaction or platform fees
- Accessing products or services
- Participating in governance and voting
- Staking to earn rewards or secure the network
When a token has clear and meaningful utility, it becomes an essential part of the ecosystem instead of just a tradable asset.
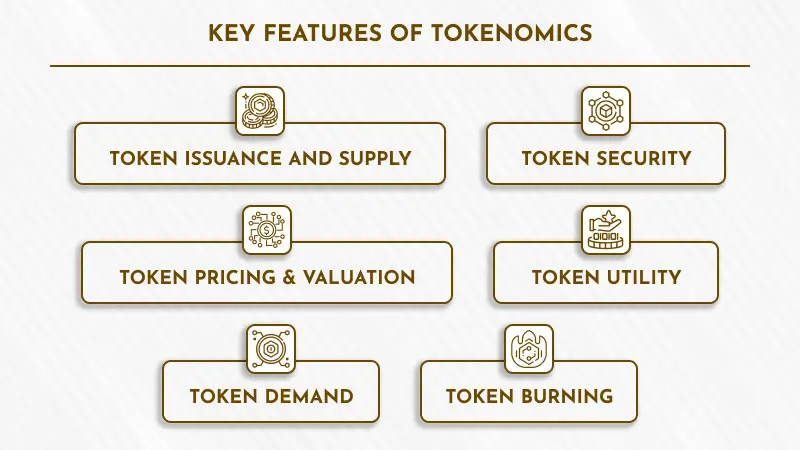
Key Features of Tokenomics
A well-structured crypto tokenomics relies on specific features that govern supply, demand, incentives, and governance to create a balanced crypto economy. These include:
Token Issuance and Supply
Token issuance refers to how and when new tokens are created. A project may plan to release its entire supply at launch or mint additional tokens over time. The supply schedule influences market confidence because it determines scarcity. When issuance rules are predictable and publicly visible, users can understand how supply might change and how that could affect future value.
Token Security
Security protects the token’s underlying infrastructure from misuse or exploitation. This includes conducting smart contract audits, implementing secure wallet storage, and using multi-signature approvals for treasury operations. It protects user interests and reinforces trust in the project’s economic foundations.
Token Pricing & Valuation
The market value of a token arises from perceived utility, scarcity, adoption, and sentiments. Tokenomics supports rational valuation by defining measurable basics rather than relying only on hype. When pricing mechanisms reflect real usage and demand, markets become more stable and less vulnerable to manipulation.
Token Utility
Utility answers the most important question: what can the token actually do? Tokens may power transactions, provide governance rights, enable staking, get access to products, or incentivize contributions. The stronger and broader the token’s utility, the more integrated it becomes within the ecosystem.
Token Demand
Demand grows when users need the token to participate in the ecosystem. Mechanisms such as staking rewards, platform-exclusive benefits, or access rights encourage active holding and usage instead of selling. Sustainable demand forms the backbone of a long-lived token economy.
Token Burning
Burning permanently removes tokens from circulation to manage inflation and maintain scarcity. Projects may burn tokens periodically or through automated mechanisms tied to usage. This controlled reduction in supply can help support token value and reward long-term participants by slowing inflationary pressure.
Different Types of Tokenomics Models
There are three major types of tokenomics models that determine how value flows within an ecosystem. Those include:
Inflationary Tokenomics Models
In an inflationary model, new tokens keep entering circulation over time. The supply grows gradually, usually to reward people who secure the network or provide liquidity.
This works like printing new money. It is useful for incentives, but inflation can reduce value if demand does not grow equally.
Examples:
- Ethereum (after moving to proof-of-stake, rewards validators)
- Polkadot and other PoS networks that regularly mint tokens
These projects mint new tokens to reward users for supporting the network.
Deflationary Tokenomics Models
Deflationary models intentionally reduce token supply to maintain scarcity. Projects may burn tokens permanently or limit maximum supply.
By reducing circulating tokens, the remaining tokens may become more valuable over time.
Examples:
- Bitcoin (fixed supply of 21M, no more minting after limit)
- Binance Coin (BNB) burns a portion of the supply periodically.
These models protect long-term value by restricting how many tokens can ever exist.
Hybrid Tokenomics Models
Hybrid models combine inflation and deflation to maintain a balance. Tokens may be minted for rewards, while another mechanism burns tokens or sets supply limits to control inflation.
This approach rewards active participants but prevents runaway supply growth.
Examples:
- Ethereum post-EIP-1559 (new ETH minted for validators, but base fees burned)
- Many DeFi ecosystems mint rewards and burn transaction fees.
Hybrid models allow supply flexibility while protecting long-term token value.
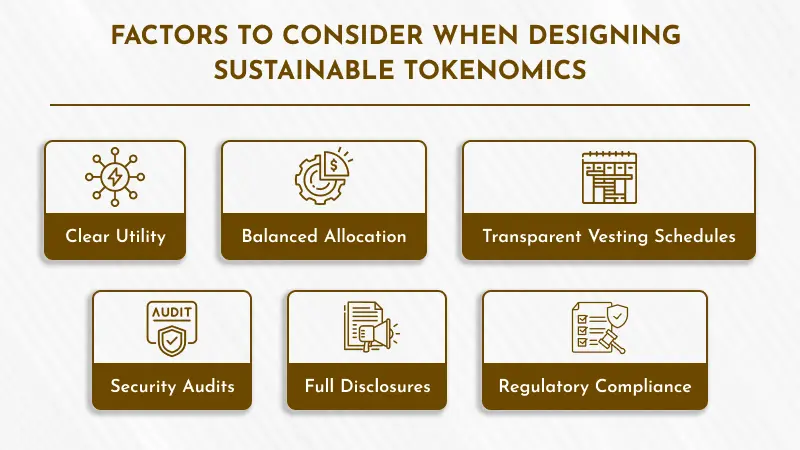
Factors to Consider When Designing Sustainable Tokenomics
Now, let’s take a look at some of the most critical factors that every blockchain project must consider before building tokenomics:
Clear Utility
A token must have a real purpose within the ecosystem. Be that it enables governance, supports a crypto payment gateway, or rewards users for participation, the token’s rol should be clearly defined. Strong utility ensures organic demand and discourages speculative trading.
Balanced Allocation
Token distribution should be fair and transparent. Developers, investors, and community members should receive reasonable allocations to avoid centralization. Proper allocation strengthens community trust, encourages governance involvement, and reduces manipulation risks such as sudden price dumps from large holders.
Transparent Vesting Schedules
Vesting schedules specify when tokens become available to team members and early investors. Well-planned vesting prevents large, immediate sell-offs and aligns insider incentives with the project’s growth timeline. Clear schedules publicly shared with the community promote credibility and long-term commitment.
Security Audits
Before launching, token contracts and supporting infrastructure should undergo thorough security audits. Independent code reviews, penetration testing, and vulnerability assessments reduce risks of exploits and protect user assets. Strong security reinforces confidence and protects the token economy from failures.
Full Disclosures
Transparency plays an important role. Projects must disclose supply details, distribution plans, burning or minting policies, and future roadmap commitments. Open communication eliminates confusion, builds trust, and allows users to evaluate risks before investing.
Regulatory Compliance
Sustainable tokenomics align with legal and regulatory expectations. Clear token classification, AML/KYC measures, and relevant licensing protect the project from legal issues, enhance investor confidence, and support institutional adoption.
The Bottom Line
That brings us to the end of this blog!
A solid understanding of crypto tokenomics distinguishes successful blockchain projects from those that are short-lived. Every token’s utility, reward model, distribution strategy, and governance structure directly influence its adoption, price stability, and community trust.
As the blockchain industry matures, investors and users are now becoming more choosy. They evaluate tokenomics before committing to a project. This makes it essential for founders and developers to build tokenomics with transparent supply mechanisms, predictable release schedules, and real economic utility.
So, if you are planning to launch a token or strengthen an existing token model, partnering with experts can make a meaningful difference. Technoloader offers end-to-end tokenomics creation solutions, from designing issuance models and governance to implementing reward mechanisms.
Let’s together build tokenomics to secure long-term success for your project!
 +91 7014607737
+91 7014607737
 info@technoloader.com
info@technoloader.com