Table of Contents
Have you ever wished that a business deal could just automatically take place without lawyers, middlemen, or endless paperwork? Sounds futuristic! That is precisely what smart contracts are making a reality.
These digital contracts have transformed our thinking about trust, transactions, and automation. What makes them “smart”, and how does the smart contract really work behind the scenes?
In this blog, we’ll break down what a smart contract is, how it works behind closed doors, and why it’s becoming a game-changer in industries far beyond crypto.
What Is a Smart Contract?
A smart contract is a self-executing digital agreement written in code and stored on a blockchain that automatically enforces terms when predefined conditions are met. It eliminates the need for intermediaries by enabling transparent, tamper-proof, and trustless transactions. Smart contracts are widely used in decentralized applications (dApps), DeFi platforms, NFTs, gaming, and supply-chain systems.
Applications built on smart contracts are commonly called decentralized applications, or dApps. Although blockchain is often thought of as the technology behind Bitcoin, it has since evolved to be so much more than that. Smart contracts can also be seen as blockchain applications that let each participant fulfill their side of a deal.
Through smart contracts, a manufacturer that needs raw materials can set up payment terms, while the supplier arranges deliveries. Consequently, according to the agreement between the two parties, funds can be automatically transferred to the seller once the goods are dispatched or received.
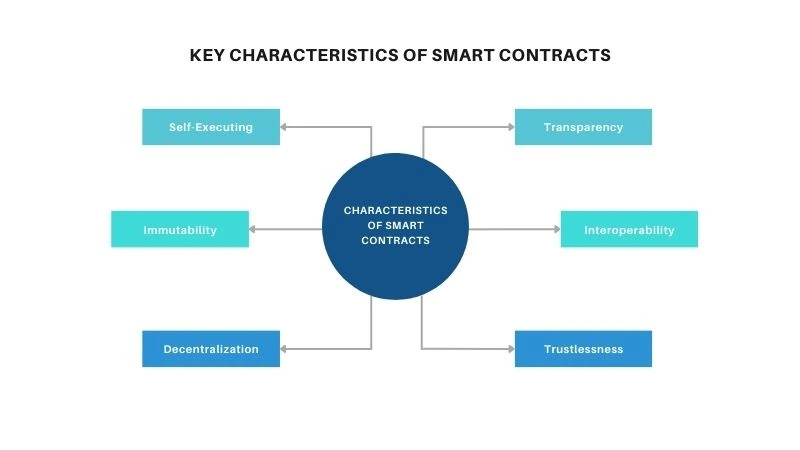
Key Characteristics of Smart Contracts
Some key characteristics of smart contracts are as follows:
Self-Executing
A smart contract is designed in such a way that it automatically gets executed once its predefined conditions are met. There’s no need for any human intervention or a third party to be involved. For example, if a smart contract is created to release payment, then once the goods are delivered, the system will automatically transfer the funds when the blockchain confirms delivery.
Immutability
After a smart contract has been written and deployed on the blockchain, it is impossible to alter or tamper with it. It is because of such immutability that the contract remains secure; nobody changes the contract rules halfway for their personal benefit. In essence, the only option is to terminate the existing contract and create a brand-new contract, an action that itself assures security.
Transparency
Participants of a smart contract can observe all rules, terms, and execution processes on the blockchain. Due to the transparency, there is no room for any ambiguity, and it keeps the parties accountable. With everything being recorded in either a public or permissioned ledger, hardly any disputes arise.
Decentralization
While traditional contracts need some central authority, smart contracts function on decentralized blockchain networks. Therefore, no single entity controls the system, making it immune to censorship or manipulation. The agreement will be implemented if the blockchain remains active and no outsider can therefore interfere, thereby assuring fairness.
Interoperability
Recently, smart contracts have been designed to work on various blockchain networks. Interoperability enables communication and execution mechanisms between different platforms; for instance, a payment on Ethereum triggers an action on a supply chain blockchain. Such cross-chain systems increase the potential for applications to be considered.
Trustlessness
In most traditional agreements, parties require some sort of trust or a third-party mediator between them, such as a bank or lawyer. Smart contracts make trust obsolete, bringing in the cover of code and cryptography. From the moment the blockchain guarantees that execution happens correctly, parties can enter into agreements completely confident, without even knowing or trusting each other.
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
A smart contract, much like a traditional agreement, creates a binding relationship between two parties. Below is a concise rundown of the stages that bring a smart contract to life.
Agreement
The involved parties must first settle on the deal’s terms and conditions. They also decide how the smart contract will function, specifying the criteria that must be satisfied for the agreement to be considered fulfilled.
Contract Creation
Either the participants build the contract themselves or work with a smart contract developer. The contractual clauses are translated into code using a suitable programming language. At this juncture, thorough security testing is essential.
Deployment
After the code is finished, it gets uploaded to the blockchain. This works just like any ordinary crypto transaction: the compiled contract is placed in the transaction’s data field. Once the network validates the transaction, the contract becomes permanent and active on the chain.
Monitoring conditions & Triggers
The contract continuously monitors the blockchain for the appearance of or an occurrence of one of the triggers or watches a trusted data feed. These triggers can be anything digitally verifiable, i.e., arrival of a specific date, receipt of payment, etc.
Execution
Once the triggering conditions are met, the actual execution of the conditional clause comes into effect, executing one or more actions like paying funds to the seller and confirming the buyer’s ownership of an asset.
Recording
Those execution results are recorded instantaneously on the blockchain. The actions undergo a process of validation by the network, which then files them as a transaction; the final state of the contract is registered on the ledger and continues to be indefinitely available.
Conclusion
Smart contracts are more than just code; they represent a significant shift in how agreements and transactions are executed. By being self-executing, transparent, immutable, and decentralized, the respective contract eliminates the need for any type of intermediary to secure trust.
The growing use of blockchain will make smart contracts essential for shaping future business, governance, and everyday digital interactions. Understanding how decentralized economies work is crucial for companies, startups, and individuals to unlock new opportunities.
If you look forward to building a decentralized application or any other Web3-related services, partnering with a well-established firm can make a difference. At Technoloader, we are committed to providing the best solutions to our clients.
FAQs
How can you use a smart contract in a dApp?
You use smart contracts in a dApp by writing and deploying them to a blockchain, using client-side libraries like Web3.js or Ethers.js to connect the dApp’s frontend to the on-chain smart contract, and then using a Web3 wallet to sign transactions and interact with the smart contract.
Can smart contracts be hacked?
Smart contracts are secure because they operate on blockchain technology. However, if the code has bugs or vulnerabilities, hackers can exploit them. That’s why audits and careful programming are critical before deployment. So technically, yes, smart contracts can be hacked.
How Smart Contracts Power Blockchain Gaming?
Smart contracts power blockchain gaming by automating the rules, transactions, and ownership of in-game assets, providing enhanced transparency, security, efficiency, and player control. They ensure all players can verify game actions on the blockchain, protect against fraud by eliminating intermediaries, and grant players actual ownership of digital items.
To learn more about how smart contracts power blockchain games, you may refer to this blog: How Smart Contracts Power Blockchain Gaming.
How do smart contracts acquire external information?
Smart contracts are unable to access the real world directly. They rely on oracles, the trusted third-party services that feed external information onto the blockchain for contract execution, such as stock prices, weather conditions, or shipment updates.
What are other applications of smart contracts?
Smart contracts offer a multitude of applications across diverse sectors, enhancing automation, transparency, and efficiency. In Supply Chain Management, they can keep tabs on products and make sure everything’s legit. In Insurance, they help speed up claims for flight delays automatically.
For further reading on use cases of smart contracts, refer to: Use Cases of Smart Contracts Beyond Crypto.
How to Audit Smart Contracts for Security?
To audit smart contracts for security, you should systematically gather documentation, use automated tools like Slither and Aderyn for initial analysis, and then conduct a thorough manual code review to identify vulnerabilities like reentrancy and access control issues.
To learn more about smart contract auditing, you may find this blog helpful: How to Audit Smart Contracts for Security.
 +91 7014607737
+91 7014607737
 info@technoloader.com
info@technoloader.com