Table of Contents
Blockchain technology has evolved into a transformative force for businesses across sectors. However, when implementing blockchain for enterprise solutions, one question inevitably arises: private blockchain vs public blockchain, which is better for your business?
This question isn’t just technical; it’s strategic. Choosing the right blockchain model determines scalability, data transparency, transaction privacy, and ultimately your competitive edge in the market.
In this blog, we’ll explore the difference between public and private blockchains, their use cases, pros and cons, and perform a comprehensive public vs private blockchain comparison to help you decide which fits your business model.
What Is a Public Blockchain?
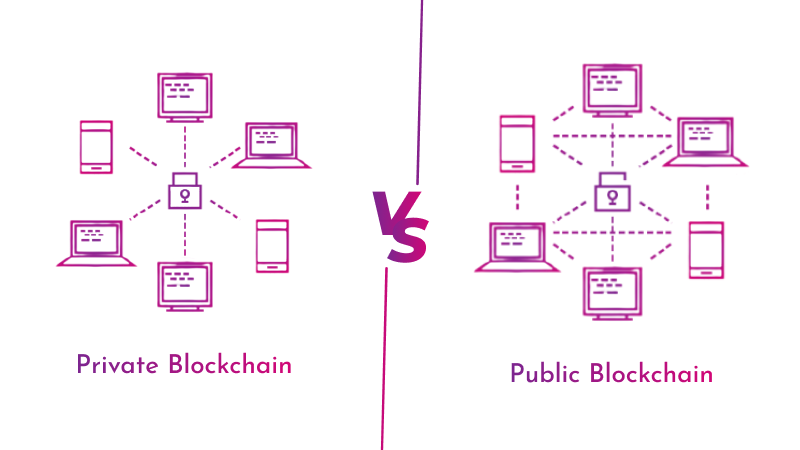
A public blockchain is a decentralized, open-source network where anyone can join, validate transactions, and contribute to the network. These are permissionless systems such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin, where every participant has equal access.
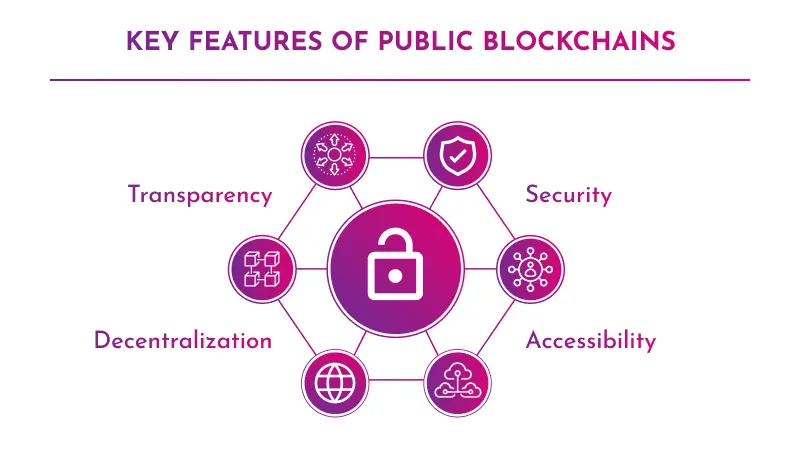
Key Features of Public Blockchains:
- Transparency
All transactions are visible on a public ledger, allowing anyone to track and verify activities in real time. This openness fosters trust among users, reduces fraud, and enhances accountability across decentralized ecosystems, particularly in finance and supply chains.
- Decentralization
No central authority controls the network; instead, distributed nodes work collaboratively to validate transactions and maintain the blockchain’s integrity. This reduces the risk of manipulation, censorship, or single points of failure, making it more resilient and trustworthy.
- Security
Public blockchains utilize advanced cryptographic techniques and consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (Pow) or Proof of Stake (PoS) to ensure that data is immutable and tamper-proof. These security measures make it highly resistant to hacking and fraud.
- Accessibility
Anyone with an internet connection can join a public blockchain without needing special permissions. This inclusivity encourages global participation, fosters innovation, and democratizes access to blockchain technology for developers, businesses, and end users worldwide.
What Is a Private Blockchain?
A private blockchain, also known as a permissioned blockchain, restricts access to specific participants. Only authorized nodes can validate transactions, read, or write data.
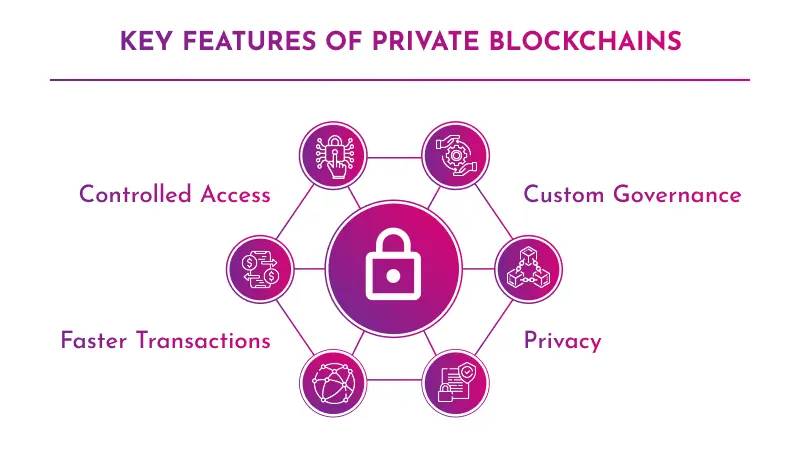
Key Features of Private Blockchains:
- Controlled Access
Only selected participants are permitted to operate nodes or validate transactions, ensuring complete control over who can access and modify data. This restricted environment enhances security, compliance, and prevents unauthorized interventions, making it ideal for enterprises.
- Faster Transactions
Private blockchains typically involve fewer nodes and less network traffic, resulting in significantly faster processing speeds. This low latency allows businesses to perform high-volume transactions more efficiently, without delays caused by global network congestion.
- Custom Governance
Organizations can define their own operational policies, permission levels, and consensus algorithms. This flexibility in governance allows businesses to create blockchain rules aligned with internal workflows, legal requirements, or industry standards for better process control.
- Privacy
Private blockchains offer a secure environment to manage sensitive information, such as financial data, health records, or proprietary business processes. Access to transaction data is limited, making it easier to comply with data protection regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
Difference Between Public and Private Blockchain
Let’s understand the core difference between public and private blockchains through the following comparison:
| Feature | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain |
| Access | Open to anyone | Restricted to authorized users |
| Speed | Slower due to network load | Faster with fewer nodes |
| Transparency | Fully transparent | Limited to permitted users |
| Security | Highly secure but slower | Moderately secure with faster consensus |
| Governance | Decentralized | Centralized or semi-centralized |
| Use Case | Cryptocurrency, DeFi | Enterprise apps, supply chains |
This public vs private blockchain comparison shows that each model serves different goals depending on the business context.
Use Cases: Public or Private Blockchain for Business?
Choosing a public or private blockchain for business largely depends on your operational needs and compliance obligations. Below are distinct use cases for each:
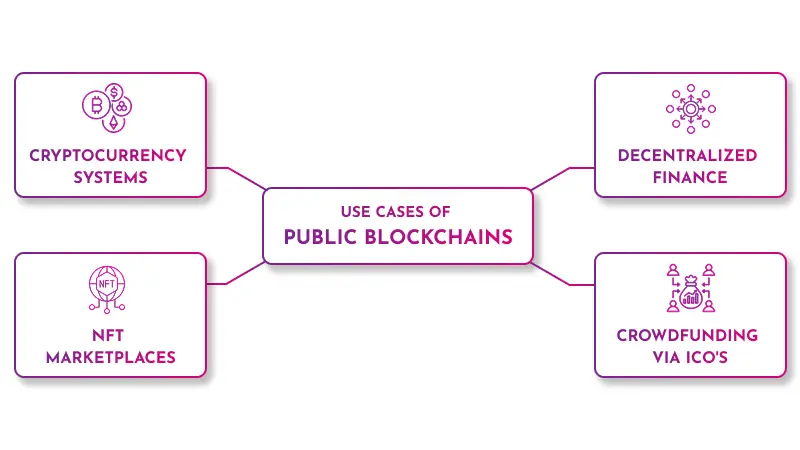
Use Cases of Public Blockchains:
- Cryptocurrency Systems (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum)
Public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum power decentralized digital currencies, enabling secure, borderless transactions without a central authority. These systems offer transparency, immutability, and accessibility to any participant globally, promoting financial inclusion and innovation.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi applications run on public blockchains to offer lending, borrowing, trading, and yield farming without traditional banks. They eliminate intermediaries, ensure transparency, and give users direct control over their assets through smart contracts.
- NFT Marketplaces
Non-Fungible Token (NFT) platforms like OpenSea and Rarible use public blockchains to authenticate ownership of digital assets. These marketplaces rely on transparency and verifiability, allowing artists, gamers, and creators to monetize content securely.
- Crowdfunding via ICOs
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) use public blockchains to raise funds by issuing tokens to global investors. They provide transparent fundraising mechanisms, enable global participation, and reduce reliance on venture capital or traditional financing routes.
Use Cases of Private Blockchains:
- Supply Chain Management
Private blockchains help track goods from origin to delivery with verified data shared among trusted parties. They enhance transparency, reduce fraud, and improve coordination across manufacturers, suppliers, and retailers in real-time.
- Healthcare Data Security
Hospitals and healthcare providers use private blockchains to store and share patient records securely. Access is granted only to authorized personnel, ensuring compliance with HIPAA and protecting sensitive data from breaches or misuse.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Private blockchains can integrate into ERP systems for better workflow automation, data sharing, and audit trails. They enhance operational efficiency across departments by ensuring accurate, tamper-proof records of inventory, HR, and finance activities.
- Financial Settlements Between Institutions
Banks and financial institutions use private blockchains for secure interbank transfers and clearing settlements. They reduce transaction time, increase transparency, and offer cost savings by eliminating redundant reconciliation processes between parties.
Also Read: Layer 1 vs Layer 2 Blockchain: Key Differences, Definitions & Advantages
Here’s another comparison to help identify which blockchain is better for business needs:
| Business Function | Recommended Blockchain Type | Reason |
| B2C Transactions | Public Blockchain | Open access and transparency |
| Internal Auditing | Private Blockchain | Data privacy and permissioned access |
| Cross-Border Payments | Public Blockchain | Decentralized and globally accessible |
| Confidential Agreements | Private Blockchain | Custom rules and restricted access |
Pros and Cons of Public Blockchain
Pros:
| Pros | Explanation |
| Decentralized and trustless environment | Operates without central control, enabling trustless interactions among participants through consensus mechanisms. |
| Ideal for global transactions | Accessible worldwide, allowing anyone to participate in secure peer-to-peer exchanges across borders. |
| Highly secure due to community validation | A large network of validators ensures strong resistance to tampering or fraud. |
Cons
| Cons | Explanation |
| Slower processing speed | Involves many validators, which slows down transaction confirmations. |
| Not ideal for confidential data | Transparency makes it unsuitable for handling private or sensitive business information. |
| High energy consumption in some consensus models | Proof-of-Work and similar protocols require extensive computing power, increasing energy usage. |
Pros and Cons of Private Blockchain
Pros
| Pros | Explanation |
| Enhanced transaction speed | Fewer nodes and permissioned access lead to faster transaction processing. |
| Better suited for compliance and privacy | Restricted access allows compliance with data protection regulations and enhanced confidentiality. |
| Customizable consensus protocols | Businesses can implement tailored consensus models to suit operational requirements. |
Cons
| Cons | Explanation |
| Centralized nature may reduce trust | Authority control may limit transparency and stakeholder trust. |
| Limited decentralization | A smaller validator base reduces network diversity and transparency. |
| Scalability challenges in complex ecosystems | Custom governance and node management can hinder scaling in large enterprises. |
Which Blockchain Is Better for Business?
The answer to which blockchain is better for business depends on whether your priority is transparency or privacy.
If your business thrives on public trust, open governance, and tokenization, public blockchain may be ideal. However, if you need speed, data privacy, and regulatory compliance, a private blockchain will serve you better.
Many enterprises today prefer hybrid models that combine the strengths of both systems, giving businesses the flexibility to operate securely and efficiently.
Public vs Private Blockchain Comparison: Key Metrics
To further clarify the difference between public and private blockchain, here’s a snapshot comparison based on business-critical metrics:
| Metric | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain |
| Ideal for | B2C, Global Use | B2B, Internal Enterprise Systems |
| Cost Efficiency | Costlier due to transaction fees | More cost-effective at scale |
| Regulatory Compliance | Less customizable | Easily aligned with business laws. |
| Smart Contract Flexibility | Limited | Fully customizable |
| Development Complexity | Moderate | High control but increased setup |
When to Choose a Private Blockchain?
You deal with sensitive information (finance, healthcare)
Private blockchains offer restricted access and strong permission controls, making them ideal for industries like finance and healthcare where secure handling of confidential records, patient data, and financial transactions is essential.
Regulatory compliance is crucial.
When your application must comply with industry regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, or financial reporting laws, private blockchains help maintain control, enforce policies, and provide auditable records while limiting exposure to unauthorized entities.
You need fast, high-throughput transactions.
Private blockchains support fewer nodes, reducing latency and increasing transaction speed. This is vital for businesses that require real-time data processing and efficient operations, especially in logistics, banking, or internal enterprise systems.
You’re building a closed enterprise app.
Private blockchains are perfect for internal business tools where only selected departments or partners need access. This ensures greater control, cost-efficiency, and integration with existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
When to Choose Public Blockchain?
You’re building for mass participation (crypto tokens, dApps)
Public blockchains are ideal for projects requiring broad, decentralized user access, such as launching crypto tokens or decentralized applications (dApps) that operate without gatekeepers or central control.
Transparency and immutability are top priorities.
If your use case demands publicly verifiable records and tamper-proof data, public blockchains ensure transparency and trust through distributed consensus and immutable ledgers that anyone can audit in real-time.
You’re entering DeFi, gaming, or NFT markets.
Public blockchains support open ecosystems crucial for DeFi platforms, blockchain-based games, and NFT marketplaces, allowing permissionless user interaction, token trading, and secure ownership tracking across a global user base.
You want global peer-to-peer interaction.
For solutions aimed at borderless engagement such as cross-border payments, token exchanges, or digital identity, public blockchains offer a decentralized network where users can interact directly without relying on intermediaries or local infrastructure.
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right Blockchain for Your Business
The debate of private blockchain vs public blockchain isn’t about which is superior, but which aligns better with your business goals. Startups, enterprises, and governments must evaluate scalability, control, and transparency needs before choosing between public or private blockchain for business.
Whether you’re focused on tokenization, data protection, or process automation, selecting the right blockchain infrastructure is foundational. Consider factors like your industry, regulatory environment, and customer engagement models before deciding.
If you’re looking for expert guidance, Technoloader is a leading blockchain development company specializing in public, private, and hybrid blockchain solutions.
With cutting-edge tools and a deep understanding of decentralized technologies, they help businesses launch secure, scalable blockchain platforms tailored to their needs.
FAQs
- What is the primary difference between public and private blockchains?
A public blockchain is open to everyone, while a private blockchain is restricted to authorized participants.
- Which blockchain is better for business use, public or private?
Private blockchains are generally better for enterprise use due to privacy, scalability, and compliance capabilities.
- Is a public blockchain secure for sensitive business data?
While public blockchains are secure, they are not ideal for handling sensitive or confidential enterprise data.
- Can businesses use both public and private blockchains?
Yes, hybrid blockchain solutions are increasingly popular and offer the best of both models.
- What are some examples of private blockchain platforms?
Popular private blockchain platforms include Hyperledger tools like Fabric, Corda, and Quorum.
 +91 7014607737
+91 7014607737
 info@technoloader.com
info@technoloader.com