Table of Contents
Are you considering to build a private blockchain network?
This sounds exciting, until you realize how many parts are involved. Choosing the right platform, setting up nodes, picking a consensus mechanism, ensuring security, and still keeping everything scalable… it’s a lot to juggle.
And if your private blockchain architecture can’t handle growth or high transaction loads, the entire purpose of using blockchain falls apart.
Be it that you are building a secure supply chain network or any enterprise-grade solution, scalability is the deciding factor for a successful blockchain deployment. The good news? With the right steps, tools, and architecture, building a scalable private blockchain network is completely achievable.
So, looking to know how to build a private blockchain?
Here’s a blog in which we’ll discuss the steps to build a scalable private blockchain network. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap you can use for private blockchain development.
Let’s get started!
Understanding Private Blockchain Networks
A private blockchain network is a permissioned version of blockchain where access is restricted to approved participants only. When we compare public blockchain with private blockchain, the former allows anyone to join, validate transactions, and view data, and the latter is controlled by an organization or consortium that defines who can participate, what roles they have, and how transactions are verified.
Because of this, private blockchains have become the preferred choice for industries such as finance, supply chain, healthcare, logistics, and government. These are the domains where sensitive data and regulatory compliance are non-negotiable.
And their adoption is growing rapidly. According to Wipro’s blockchain survey, 40–60% of organizations that have deployed blockchain solutions are using private blockchain networks, largely due to their performance, privacy, and operational control advantages.
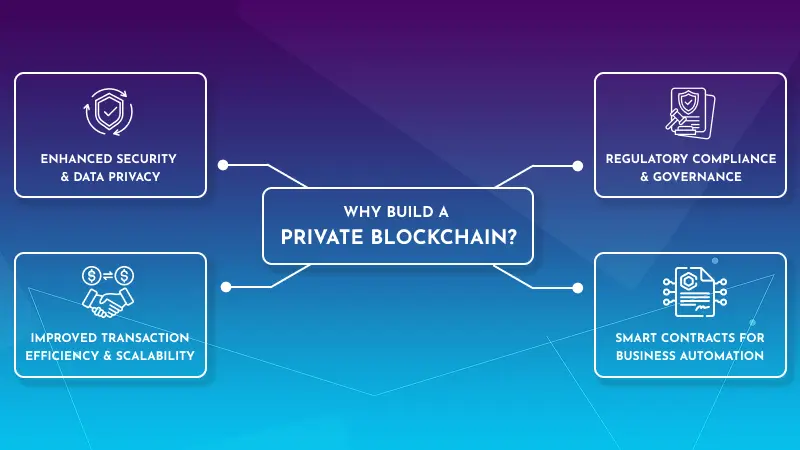
Why Build a Private Blockchain?
Before we move on to steps, let’s check out the benefits of private blockchain for business:
Enhanced Security & Data Privacy
Data security and privacy are some of the reasons why businesses adopt private blockchain networks. They help protect private data, and these provide several security features, which reduce data breaches and security threats.
Here’s how private blockchains boost security:
- Encryption: They use advanced cryptographic techniques to protect transactions, which ensure data is secure and immutable.
- Permissioned Access: It allows only authorized members to access and modify data, which prevents unauthorized interference.
- Limited Cyberattacks: Due to the fact that private blockchain networks operate in a closed ecosystem, they are less vulnerable to hacking and 51% attacks.
Regulatory Compliance & Governance
In many industries, strict regulatory frameworks require businesses to follow specific data security standards, financial regulations, and compliance protocols. A private blockchain network enables enterprises to meet these requirements effectively by offering controlled access and auditability.
Here are the compliance benefits of private blockchains:
- Regulatory Compliance: Private blockchain networks are designed to meet KYC, GDPR, AML, HIPAA, and more financial regulations.
- Governance Control: Enterprises often define rules, policies, and access levels, which ensure only authorized members can approve transactions and amend records.
- Auditability: Every transaction is recorded on the blockchain, which makes it easy for regulators and auditors to track activities.
Improved Transaction Efficiency & Scalability
Public blockchains often struggle with transaction speed and scalability-related issues. The presence of many thousands of nodes in a public blockchain network is a major reason for delays and congestion, often resulting in high transaction costs.
So, here’s why private blockchains offer better performance:
- Faster Transactions: Because only a few authorized nodes participate in the consensus, transactions are confirmed instantly.
- Optimized Resource Utilization: Private blockchain networks allocate resources efficiently, which ensures smooth performance.
- Lower Transaction Costs: Enterprises can avoid higher gas fees as compared to public blockchains.
Smart Contracts for Business Automation
Smart contracts are one of the best features in private blockchains. These are self-executing contracts that allow enterprises to automate agreements, minimize paperwork, and boost security.
Some of the potential benefits of smart contracts in private blockchain include:
- Automated Execution: The smart contracts execute automatically when a predefined set of rules are met, which mitigates the need for manual approval.
- Error Reduction: By using smart contracts, enterprises can reduce human errors and disputes.
- Immutable Agreements: Smart contracts function on blockchain, which ensures that the terms can’t be modified.
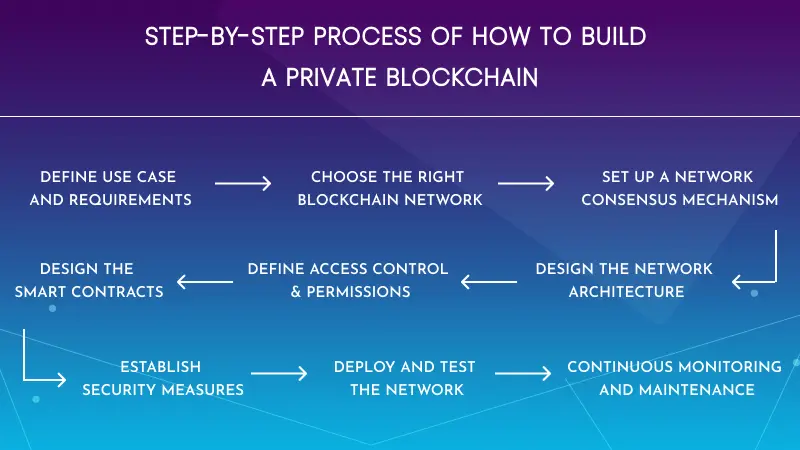
Step-by-Step Process of How to Build a Private Blockchain
Here’s the most important part of the blog. Now, let’s talk about the steps to build a private blockchain in detail!
Step 1: Define Use Case and Requirements
Before selecting a blockchain network or designing a scalable blockchain architecture, the first step is to clearly define why you need a private blockchain and what it is expected to achieve. A well-defined use case lays the foundation for building a scalable and efficient private blockchain network.
Start by identifying the problem you want to solve. Ask questions such as:
- What process needs transparency, automation, or trust?
- Who are the participants involved in the network?
- What type of data will be recorded on the blockchain?
- Does the data require strict privacy or selective access?
Next, outline your requirements. This includes defining transaction volume, expected network growth, performance targets, data storage needs, and compliance obligations. Understanding these parameters early helps avoid scalability issues and costly redesigns later.
Step 2: Choose the Right Blockchain Network
The next step is selecting the right blockchain network to build your private network.
Different platforms are designed to solve different enterprise needs. When choosing blockchain networks, consider factors such as scalability capabilities, consensus mechanisms, smart contract support, ease of integration, and community support.
Popular networks commonly used for private blockchain networks include:
- Hyperledger Besu: An Ethereum-based option that supports both public and private networks, useful if you want Ethereum compatibility.
- R3 Corda Enterprise: The commercial version with additional features for production deployments.
- Private Ethereum networks: Using Geth or Parity with PoA consensus for organizations already invested in the Ethereum ecosystem.
Step 3: Set Up a Network Consensus Mechanism
The consensus mechanism is the core engine of a blockchain network. It determines how transactions are validated and how agreement is reached among participating nodes. In a private blockchain, choosing the right consensus mechanism is essential for achieving high performance, reliability, and scalability.
Depending on your needs and goals, you need to choose a consensus mechanism. Unlike public blockchains that rely on energy-intensive models such as Proof of Work (PoW), private blockchain networks can use more efficient consensus algorithms because participants are known and trusted.
Common private blockchain consensus mechanisms include:
- Proof of Authority (PoA): Ideal for enterprise environments where validators are pre-approved.
- Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT): Designed to handle faulty or malicious nodes while ensuring consistency.
- RAFT: RAFT consensus for private blockchain is lightweight and efficient, suitable for networks that require fast finality and simple fault tolerance.
- Kafka-based consensus: Often used in permissioned blockchain networks to support high-volume transaction processing.
Step 4: Design the Network Architecture
The next step is designing the network architecture. It defines how your private blockchain will operate, communicate, and scale over time. A strong architecture prevents issues, improves resilience, and makes future scalability smoother.
Start by defining blockchain node roles clearly. In a private blockchain, not every node needs to do everything. Depending on your platform, you may have roles such as:
- Validator/Consensus nodes (validate and finalize transactions)
- Peer/Participant nodes (submit transactions and maintain ledger copies)
- Observer/Read-only nodes (view data without validating)
- API gateway or client nodes (connect external apps to the network)
Step 5: Define Access Control & Permissions
One of the main benefits of private blockchain networks is the ability to control access and permissions. In this step, you need to determine who can participate in the network, create new blocks, access sensitive data, and more. Also, implement access control mechanisms, which include private keys, to ensure only authorized participants can perform certain actions on the private blockchain.
This includes:
- Participant’s Role: Define the role of specific participants in the blockchain network.
- Cryptographic Keys: Set up private keys to restrict access to confidential data.
- Governance Model: Establish a governance model to enforce access control and permissions.
Step 6: Design the Smart Contracts
Basically, smart contracts are self-executing contracts with predefined terms written directly into code. The next important step is to start designing smart contracts that help automate processes and agreements within the network. It reduces the need for third parties, cuts down transaction times, and ensures the seamless and smooth execution of business operations.
In the development lifecycle, these smart contracts can be customized to suit the particular needs and goals. Creating and deploying smart contracts is important to ensure your private blockchain solution performs seamlessly, smoothly, and efficiently.
Step 7: Establish Security Measures
Before enterprise blockchain deployment, it is important to put strong security measures in place to protect data, transactions, and network participants. Since private blockchains often handle sensitive and regulated information, security must be addressed at all levels.
By establishing strong security measures before deployment, enterprises can protect their private blockchain network and build a trusted base for long-term scalability and adoption.
Step 8: Deploy and Test the Network
Once done with the above-mentioned steps, you need to deploy your private blockchain network on the selected network. Test the network’s functionality, performance, and security functionalities to ensure that it meets your specific needs and goals. Conduct end-to-end testing and resolve any issues or bugs.
Some of the important tests that you need to conduct include:
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Conduct testing with the audience to ensure that the private blockchain meets their needs.
- Load Testing: You need to test the network’s scalability and performance under various load scenarios.
- Security Testing: Test the blockchain network’s security features and identify and fix any bugs found.
Step 9: Continuous Monitoring and Maintenance
Deploying a private blockchain network is not the end of the journey. To ensure long-term reliability, security, and scalability, continuous monitoring and maintenance are important.
Start by implementing real-time monitoring tools to track network health, node performance, transaction throughput, latency, and error rates. Monitoring these metrics allows teams to detect bugs early and respond before they impact business operations.
Regular maintenance activities should include updating nodes, applying security patches, optimizing configurations, and reviewing access permissions. As the blockchain ecosystem evolves, keeping the network up to date ensures compatibility, stability, and improved performance.
Wrapping Up
That’s a wrap for this blog!
Building an enterprise private blockchain is a crucial step for businesses aiming to leverage the benefits of blockchain technology while protecting sensitive information.
By following this private blockchain setup guide, you can easily build and deploy your private blockchain infrastructure with enhanced security and privacy.
Still in doubt? Don’t worry!
We, at Technoloader, a known private blockchain development company, specialize in this field and provide custom solutions to suit your specific needs and goals. Our team of professionals possesses extensive knowledge and experience to guide you through building and deploying a private blockchain network.
Get in touch with us to know how we can help you build secure and scalable private blockchain infrastructure!
FAQs
What is the difference between a private blockchain and a public blockchain?
A public blockchain is open to anyone, which allows unrestricted participation and data visibility. On the other hand, a private blockchain is permissioned and controlled by an organization, and offers better privacy, governance, and performance for enterprise use cases.
Can a private blockchain network scale effectively?
Yes, a private blockchain can scale efficiently when designed correctly. By choosing the right platform, consensus mechanism, and network architecture, private blockchains can handle high transaction volumes while maintaining performance and security.
Which industries benefit the most from private blockchain networks?
Industries such as finance, supply chain, healthcare, logistics, insurance, government, and manufacturing benefit due to their need for secure data sharing, auditability, and compliance.
How long does it take to build a private blockchain network?
The timeline varies based on complexity, use case, and integrations. Get in touch with our experts to get an estimated timeline!
Is a private blockchain more secure than a public blockchain?
Private blockchains offer enhanced control and restricted access, which improves security in enterprise environments.
What platforms are commonly used to build private blockchain networks?
Popular platforms include Hyperledger Fabric, Quorum, Corda, and MultiChain and each of them offers features tailored to different enterprise needs and goals.
 +91 7014607737
+91 7014607737
 info@technoloader.com
info@technoloader.com